Metrology
Metrology
Metrology is the science that studies measurement systems. If we assume that measuring means comparing two elements and assigning them a number or value, metrology is responsible for selecting what will be measured, and then choosing the units and instruments used for the measurement. When comparing two elements, a standard is used as a reference for the measurements, in order to balance other instruments.
In which sectors is metrology applied?
All objects, surfaces, planes, and levels that can be measured use measuring instruments to assign them a value. Sectors where metrology is applied include manufacturing and industry, parts assembly, construction , and automotive, among others.
The International System of Units (SI) currently exists, which is composed of seven basic units that are perfectly applicable to any work process, both in the professional field and in daily life. Each of these units has its own unit.
Magnitudes and units
- Length: Meter.
- Mass: Gram.
- Time: Second.
- Temperature: Kelvin.
- Luminous intensity: Candela.
- Amount of substance: Mol.

Classification of metrology tools
Metrology can be classified into three types depending on the field in which it is applied:
Legal metrology
This branch of metrology governs all aspects related to the laws and regulations a country establishes regarding measurement units, ensuring that measurements are applied correctly and that there is healthy competition among merchants.
Scientific metrology
It deals with all technical aspects of metrology. Its scope includes verifying the functioning of measuring instruments, maintaining standards, and researching other measurement techniques.
Industrial metrology
Within the industrial field, metrologists are responsible for adjusting, calibrating, and verifying various measuring instruments. Instrument adjustment refers to the maneuvers performed so that it can provide instructions consistent with the values to be measured. Calibration establishes a relationship between an instrument's values and the potential margin of error reported by a manufacturer's standard or according to pre-established regulations. Verification consists of comparing the values of a piece of equipment with a previously calibrated instrument.

Measuring instruments
Among the instruments used in the different areas of metrology are:
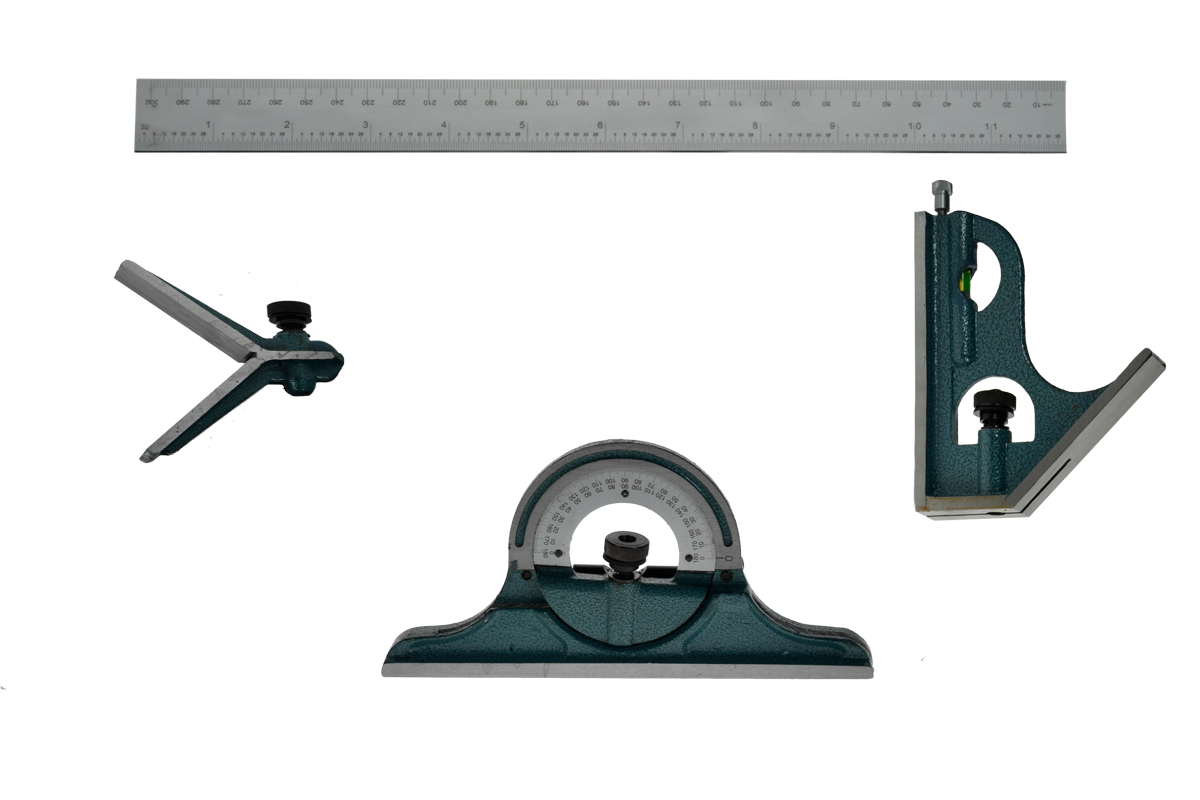
| Ruler |
The ruler is a rectangular instrument, which can be rigid or foldable, and is used to draw length measurements on different surfaces. Their length can vary between 1 and 2 meters, and measurements are on a graduated scale, indicated by decimeters, centimeters, millimeters, and some even have inches. |
| Metro |
The meter or tape measure, also divided into the measurement scale, is a flexible instrument that has a steel blade at both ends. They can also be rolled up inside a plastic or metal casing. Some have an anchor that locks the unit to prevent it from moving. |
| Plumb |
It is a cylindrical weight with a conical tip, which hangs from a rope. It is used to measure and indicate that all work is vertical and its distributed weight is stable, taking the law of gravity as a reference. |
| Caliber |
Also called a vernier caliper, it consists of a ruler with a set square at one end and a second scale called a "nonius" or "Vernier scale." This instrument is used to measure interiors, exteriors or depths, thanks to its depth probe. |
| Level | The level is a plastic or glass tube filled with a liquid and a bubble, which will indicate whether an object is balanced horizontally or vertically, when the bubble is stable between the two marks on the level. |
| Squad | A set square is a piece or template in the shape of a right-angled or isosceles triangle. It's used to draw straight lines and is ideal for joining the angles of two surfaces or objects. |
| Protractor | A goniometer, protractor, or angle protractor is a semicircular instrument with a scale graduated in 180° or 360°. It is used to construct and measure the angles of objects. |
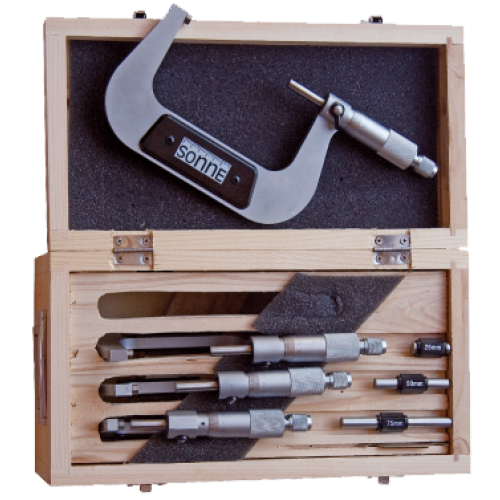
| Micrometer |
Also known as the Palmer screw, the micrometer is used to measure the dimensions of an object with exacting precision. To do this, it uses a micrometer screw, which consists of a threaded screw with an engraved scale for measuring. Its scale measures in nanometers and millimeters, and it is considered the most precise instrument. |
| Durometer |
This tool is used to measure the hardness of different materials, using a ball or point indenter. The measurement is made by applying pressure to the objects and thus defining the resistance of the material. |
| Scriber | The height gauge or scribing gauge is an instrument used to measure the height of different pieces, planes, or levels. It consists of a column with a built-in scale graduated in millimeters and centimeters, and a caliper used to mark the height of the pieces. |