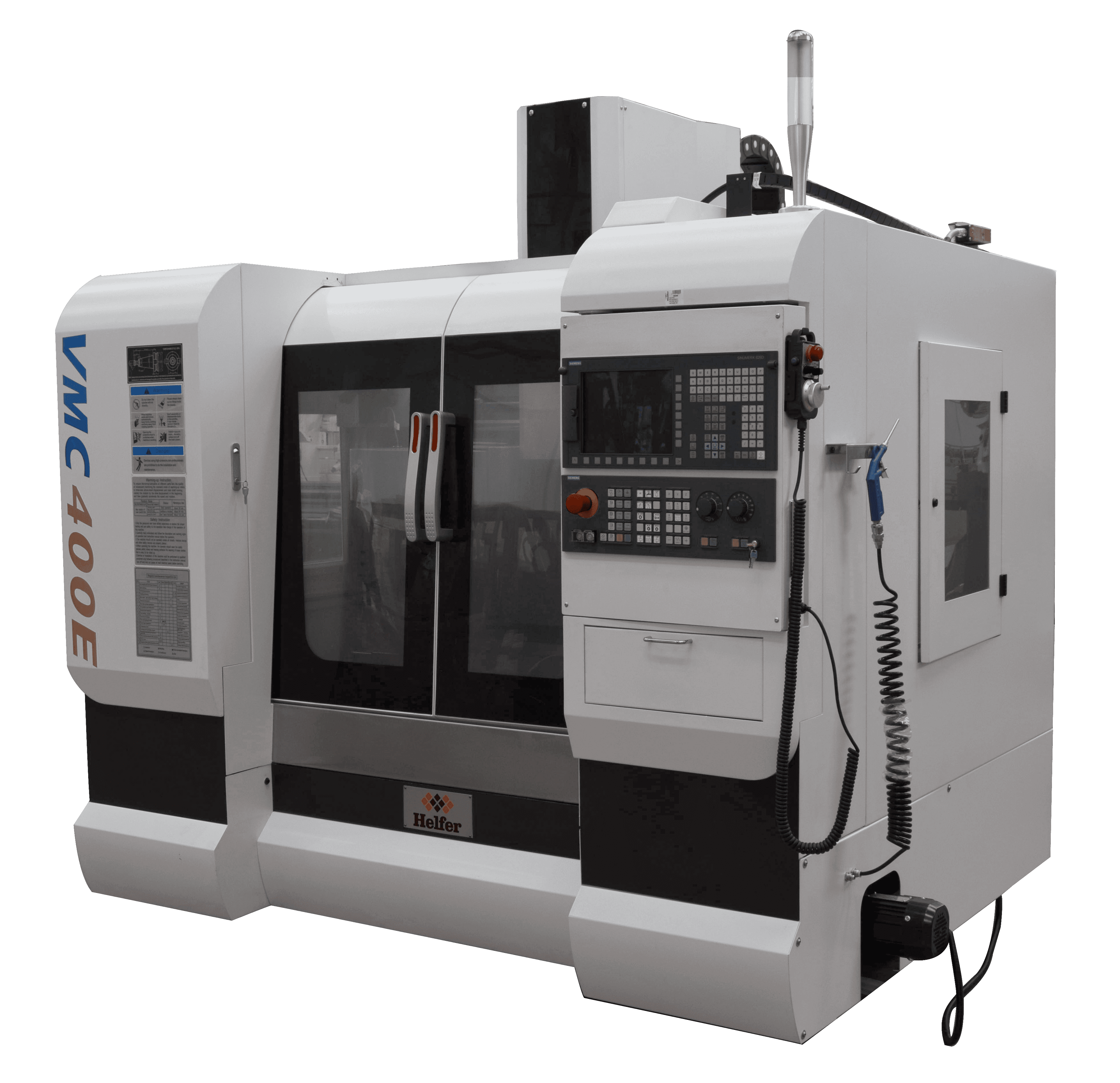
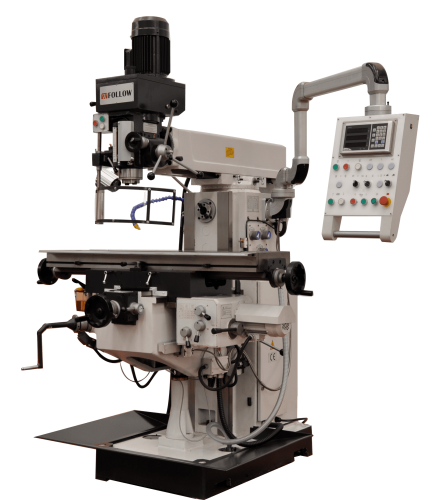
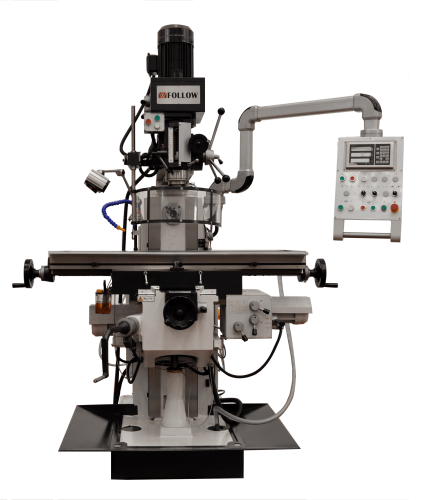
Conventional Milling Machines
What are conventional milling machines?
Conventional milling machines are a type of machinery that allows for the execution of mechanical manufacturing processes. These processes are carried out using a chip removal system, which consists of the movement of a rotating tool equipped with different cutting edges.
The milling cutter, as the rotating tool is called, is used for mechanical milling of industrial materials such as steel, non-ferrous metals, wood, cast iron, curved and flat surfaces, and synthetic materials, among others. If desired, conventional milling machines can also be used to refine or roughen materials.
Conventional milling machines operate by moving the workpieces until they approach the cutter. This allows for different shapes to be obtained, depending on how the approach is made. Flat surfaces are the easiest to create, but they also offer the possibility of producing more complex shapes.
Components of conventional milling machines
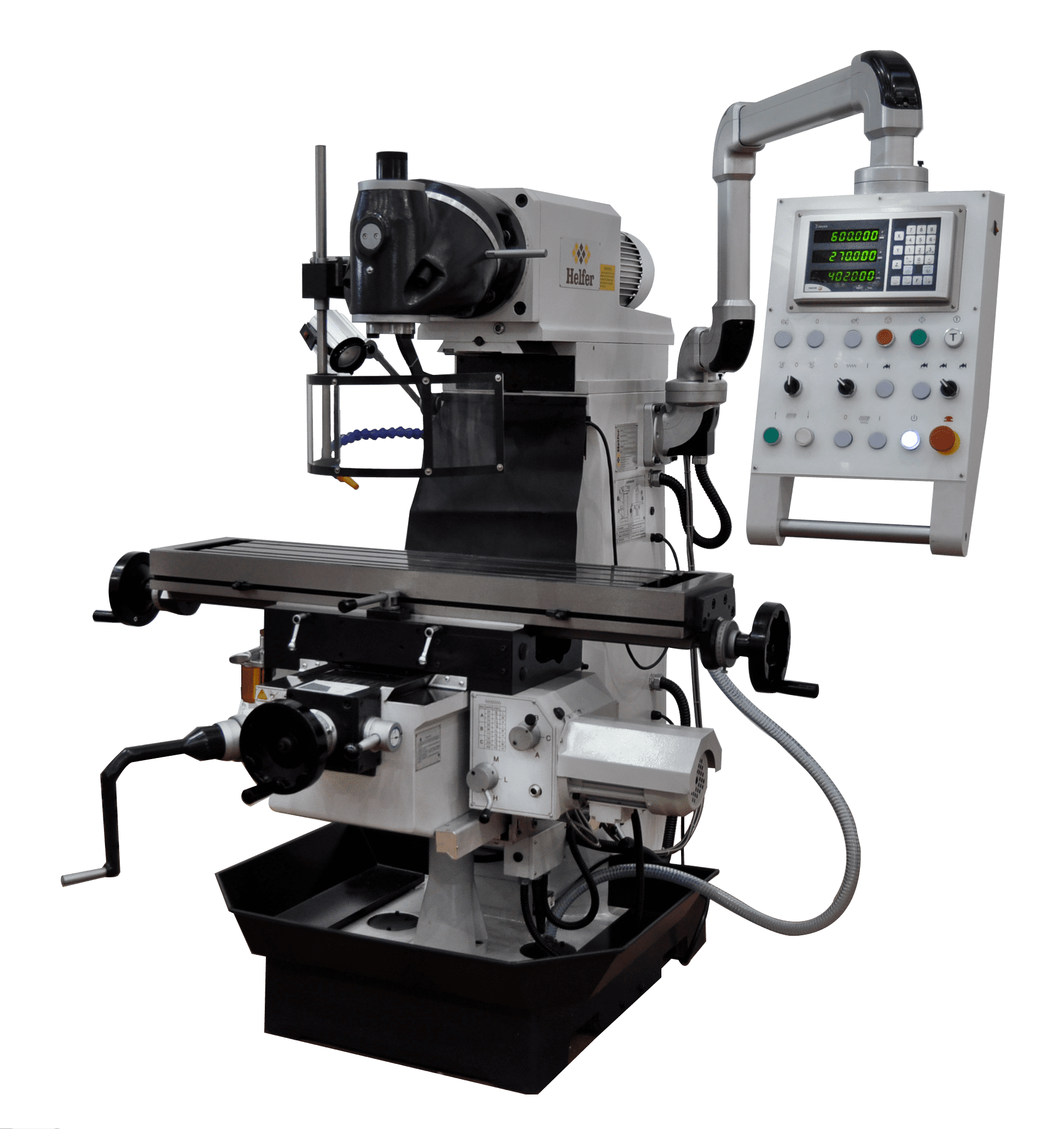
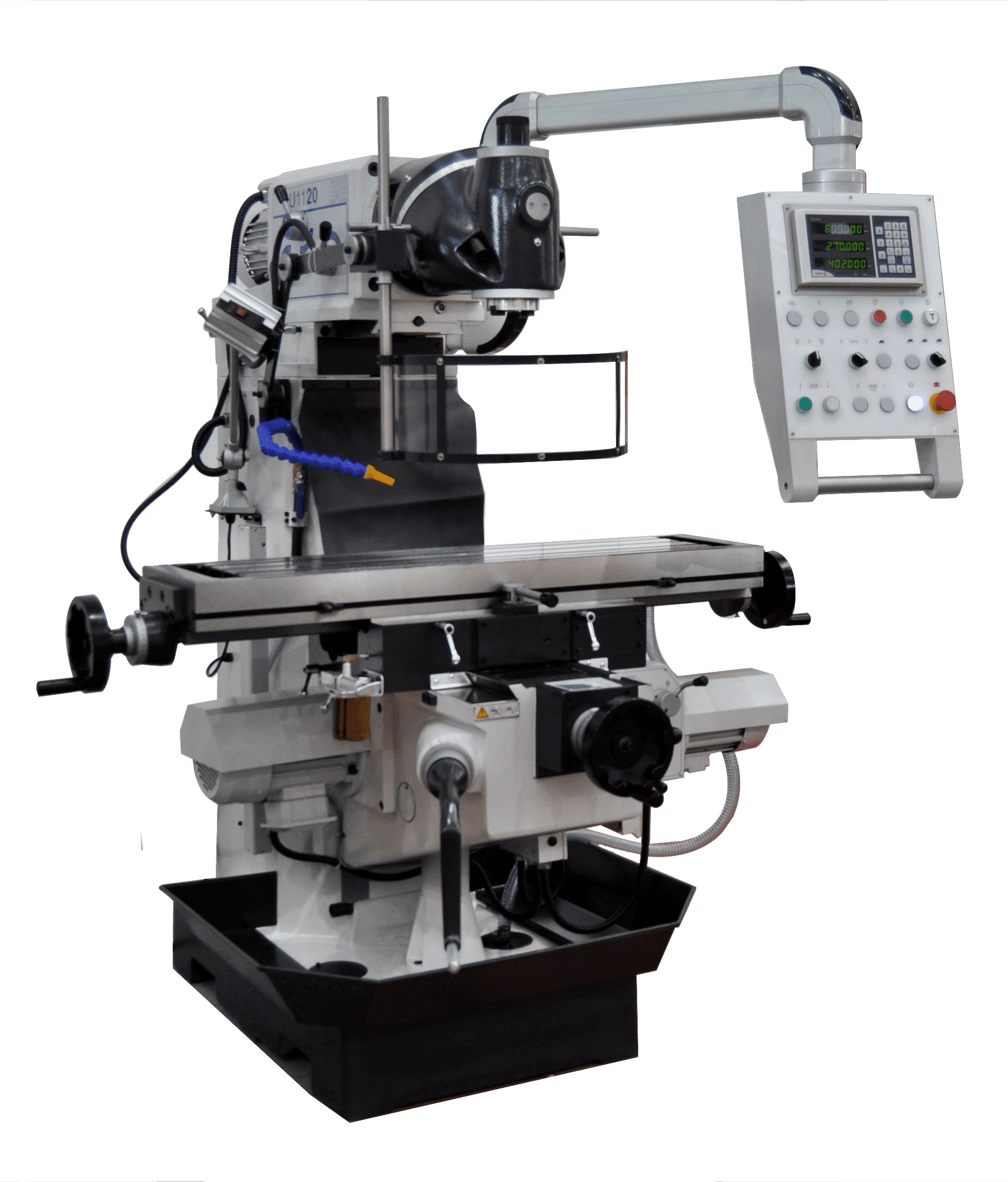
The most important components of conventional milling machines are the carriage, bridge, table, tool holder, body, base, and console. Each of these components has a function that allows the milling machine to function properly.
Base
The function of the base is to ensure that the conventional milling machine is properly supported on the floor, so that it does not move while in use.
Body
The body rests on the base or, sometimes, forms part of it. It is column-shaped, stable, and usually made of alloy casting. It has ground and tempered guides on the front to allow the console to operate. It also includes controls for controlling the machine and its actions.
Console
Its main function is to hold the table, so it slides vertically along the body guides.
Table
The table must rest on the carriages responsible for the transverse and longitudinal movement performed on top of the console. It also has a slot in the surface in which the workpiece can be held.
Bridge
This is a piece that rests on the cantilever frame. The bridge has rests where the tool spindle can be supported. It also tends to have at least one eyebolt on the top, the sole purpose of which is to make the conventional milling machine easier to transport.
Tool holder
The tool holder, also known as the milling cutter, is the support for the milling cutter, as it is responsible for executing the rotary motion generated by the mechanisms located in the body. It is usually made of a chrome-vanadium alloy and steel.
Accessories available for conventional milling machines
There are a variety of accessories available on the market for conventional milling machines, each designed to enable the performance of specific mechanical tasks or to improve the safety, precision, efficiency, and speed of the machines. These include:
Axle adding devices
These are used to alter the way tool holders are added. These include the rotary indexing table, the universal indexing table with tailstock, and the multi-angle head.
Devices for holding workpieces
These accessories are used to alter the way parts are held on the bridge. These accessories include the hydraulic vice, the rotating and graduated vice, the tailstock and steady rests, and the three-jaw universal chuck with counter-plate.
Functions of conventional milling machines
The primary function of conventional milling machines is to facilitate the manufacture of angular and flat surfaces, although they can also be used to create irregular surfaces. They can also be used for cutting samples and slots, drilling, reaming, cutting gears, boring, and machining previously manufactured surfaces.
What advantages are obtained with milling machines?
This machinery offers advantages when performing milling tasks compared to manual milling. Some of these advantages are listed below:
- They offer the highest precision that can be achieved in mechanized manufacturing processes.
- They allow the production of uniform materials in mass.
- Several conventional milling machines can be used by a single operator.
- They allow multiple milling processes to be carried out in the shortest possible time.
- They facilitate the production of complex products.
- They optimize work efficiency.
- They ensure that quality control can be kept tight at high levels.
- They have a fairly low risk of injury to operators.
- They allow for excellent quality of work performed, based on good scheduling and organization.